What Does a ProblemOps Specialist Do?
A ProblemOps Specialist is the bridge between business functions. They build systems of shared understanding, empower change, and inspire teams to make change incrementally. In this article, get a cheat sheet to explain what a ProblemOps specialist is and does.

Overview
In this article, get a cheat sheet to explain what a ProblemOps specialist is and does.
Defining "ProblemOps"
Read the introduction to the discipline before reading this.
ProblemOps stands for "Problem-solving Operations". It is a people-first approach to innovation. It describes a system of language building approaches that help teams build shared understanding and carry out change together.
Areas of Expertise
- Operations
- End-to-End Experience
- Strategy
- Delivery
Key Skills that Make a Great ProblemOps Specialist
- Written and verbal communication
- Collaboration
- Process management
- Problem-solving
- Experience mapping
- Facilitation
- Requirements gathering
- Requirements writing
- Go-to-market strategy
- Strategic thinking
Duties
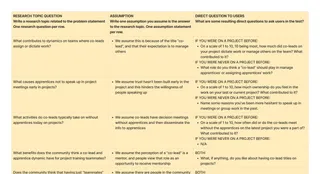
If a ProblemOps Specialist is what we're called, what are we expected to actually do? It's a mix of "roles", otherwise known as "duties". If you can imagine hat, you wear many hats as a ProblemOps Specialist:
- Product Owner duties
- Product Manager duties
- UX Research duties
- UX Design duties
- Business Analysis duties
- Product Operations duties
Daily Responsible Activities
- Creating scenario-based problem statements.
- Writing, gathering, and refining instructions for delivery (AKA requirements) with teams:
- Acceptance criteria
- User stories
- User goals
- User needs
- Task-level scope
- Flow charts
- Rallying teams around a common vision and scope.
- Identifying, validating, and testing assumptions being made by teams and leadership.
- Documenting the current state of the world before the change is made.
- Mapping end-to-end experiences based on the desired change.
- Creating measurements of success based on the desired change.
- Working with teams to track the delivery of the change.
- Inspiring teams to own their own process of continuous problem-solving.
- Coaching the practices of continuous problem-solving operations.
Common Deliverables
- Scenario-based problem statements
- Vision boards
- Release plans
- Positioning statements
- Use case scenarios
- Research
- Requirements
- Flow charts
- Success measurements
Methods
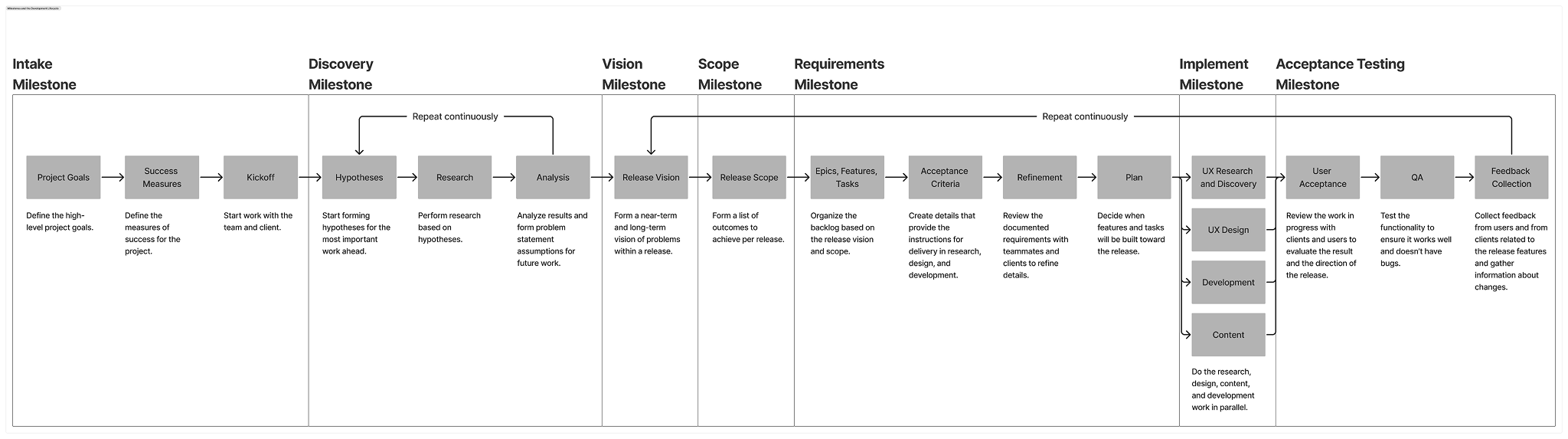
The benefit of the ProblemOps system is that methods can be applied modularly within its system. The cycle of building products and services never stops, and ProblemOps exists within the entire cycle of work. From intake to delivery to identifying next steps and change.
What ProblemOps Specialists do is build a shared language of understanding, commit to work, and track change that matters.
How ProblemOps Specialists perform the work is up to them and their context.
Here's a common way to think about project lifecycles:
- Intake
- Discovery
- Vision
- Scope
- Requirements
- Implement
- Test
ProblemOps exists within this whole lifecycle.
Continuous Delivery
ProblemOps specialists do this work in parallel to follow incremental deliver work. Find out more about the operations of continuous problem-solving here:

Find out more here: https://www.problemops.com/continuous-problem-solving-operations/. Credit: ProblemOps.